Explore your charging and installation options
Charging your electric vehicle (EV) is easier than ever with options for home, work, and public stations. Learn about the types of chargers available, how to get set up, and more!

Types of Electric Vehicle Chargers
Electric vehicles can be charged using three main types of chargers. Each level varies in speed and is suited for different locations and lifestyles.
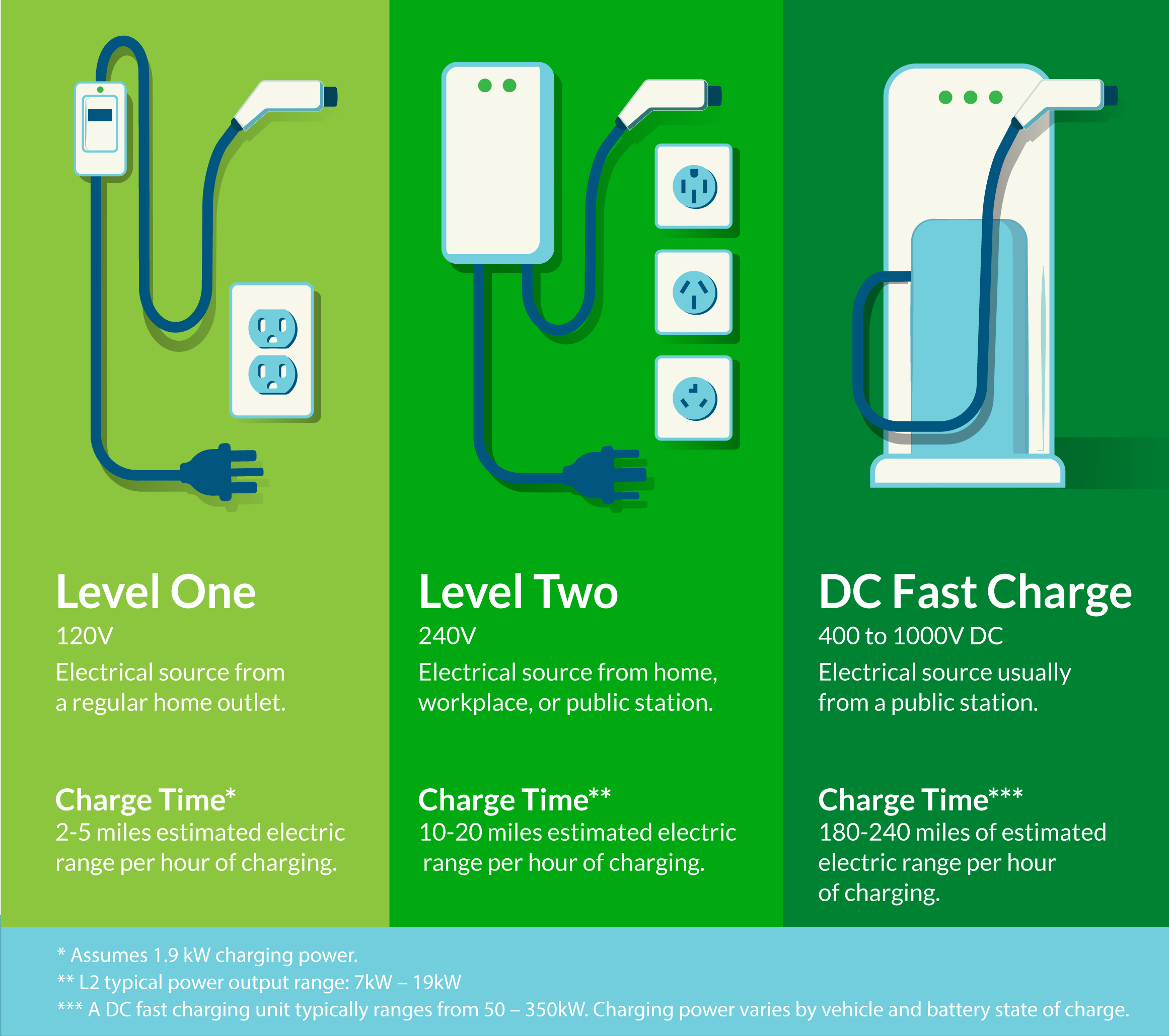
Level 1
Level 1 chargers use your EV’s standard charging cord and plug into a common wall outlet, available in most garages or driveways. While slower, this method can still support 40+ miles of driving per day when used overnight. It’s a great option for low-mileage drivers or as a backup charging solution.
- Power Source: Standard 120V household outlet (no installation required)
- Where You’ll Use It: At home, typically overnight
- Charging Speed: Adds about 2-5 miles of range per hour
- Full Charge Time: 40-50 hours for a 60 kWh battery
- Good For: Short daily commutes; drivers who can charge overnight
Level 2
Level 2 chargers require additional equipment and installation by an electrician, though some homes may already have a 240V outlet available. They’re also widely available in public locations. Many EV owners install Level 2 chargers at home for faster, more convenient daily charging.
- Power Source: 240V outlet
- Where You’ll Use It: At home (with installation), workplaces, and public charging stations
- Charging Speed: Adds about 10-20 miles of range per hour
- Full Charge Time: 4-10 hours for a 60 kWh battery
- Good For: Daily drivers, longer commutes, or faster overnight charging
DC Fast Charge
DC Fast Chargers are the fastest option, ideal for long trips or when you need a quick charge.
- Where You’ll Use it: Public stations, along highways, at commercial sites
- Charging Speed: Adds about 180-240 miles of range per hour
- Full Charge Time: Some EVs can reach up to 80% in as few as 20 minutes – 1 hour
- Good For: Road trips, quick charging or top ups
While safe to charge to 100%, speeds slow down significantly after 80% state of charge (SOC), so charging up to 80% is usually most efficient. Also, be sure to check your EV’s charging capacity, some vehicles may not accept higher kW rates even if the station offers them.
Charging Time Basics
Charging time depends on two key factors:
- How much energy (kWh) your EV battery needs, based on battery size and current state of charge (SOC)
- The power output of the charger you’re using (measured in kilowatts or kW)
Other factors that impact charging speed include the temperature of the battery, other loads in use while charging such as heating or cooling the cabin, battery deterioration, and the vehicle’s current and voltage limits.
Estimate Your Charging Time
You can estimate your charging time using this formula:
Charge needed (kWh) / Charger power (kW) = Hours of charging time in hours
Step-by-Step Example:
Let’s say you drive a Tesla Model 3 with an 80 kWh battery. Your battery is currently at 20%, and you want to charge it up to 80% using a Level 2 charger that provides 7.68 kW.
Step 1: Find the percent of charge needed
80% (target) – 20% (current) = 60% needed
Step 2: Convert that percentage to kilowatt-hours
80kWh x 0.60=48kWh needed
Multiply your total battery size by the percentage of charge you want to add (60% = 0.60)
Step 3: Use the charging time formula
48kWh / 7.68kW = ~6.25 hours of charging
Tip: You can use this same formula with any charger and vehicle, just swap the correct battery size, percent needed, and charger power.
Home Installation
Most EV owners charge at home. Level 1 chargers plug into a standard 120V household outlet and are great for overnight charging. For faster charging, Level 2 chargers require a 240V outlet and usually need professional installation.
Equipment & Installation
Installing a Level 2 charger at home is a popular option for EV drivers who want faster, more convenient daily charging.
Level 2 Charging Station Costs
- Charger Cost: A single-port Level 2 charger (7.2kWh/240V/40A) typically starts at $500
- Installation cost:
- Single-port charger: $400-$1,700
- Dual-port charger: $800-$3,400
- Costs vary based on your electrical panel, distance from the outlet, and whether new circuits are needed.
- For more information on cost, check out this article from HomeAdvisor.
Permit Fees:
- Local permits are usually required before installation, and may cost between $160-$300. Check with your jurisdiction for specific permitting instructions and prices.
Need help finding a certified electrician? Use the Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Training Program’s (EVITP) Find a Contractor Tool.
Choosing a Home Charger
When choosing a home charging station, consider the features, installation method, and location that best fits your needs.
There are two main types of Level 2 chargers:
- Plug-in chargers, which plug into a 240V outlet (such as NEMA 14-50 or NEMA 6-50)
- Hardwired chargers, which are permanently connected to your home’s electrical system.
Plug-in chargers do not require installation and can be relocated, while hardwired chargers are typically required for outdoor installations.
Amperage & Charging Speed:
- Home chargers range from 16 to 50 amps. Higher amperage allows for faster charging but may require electrical panel upgrades.
- The charging speed is directly related to amperage – more amps generally means fewer hours to reach a full charge. A 32 amp level 2 charging station adds about 25 miles of range per hour of charging.
Where to Install Your Charger:
- Chargers can be installed indoors (in a garage) or outdoors.
- Outdoor installations may require a weatherproof charger and a hardwired connection.
Other Features to Consider:
- Some chargers include smart features like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity so you can start, stop, and monitor charging from your phone. These tools can help you optimize efficiency and reduce costs over time.
- Installing solar panels to power your charger may allow your EV to run fully emissions-free.
For more information, check out the AFDC’s Charging EVs at Home page or this article from Consumer Reports.
Incentives & Rebates
Maryland Home Charger Rebate Program
Maryland offers a rebate program that may help offset the cost of purchasing and installing a home EV charger.
Utility EV Charging Programs
Your electric utility may also offer special rates, rebates, or smart charging programs for EV owners. Programs from BGE, Pepco, and Potomac Edison could help reduce your home charging costs.
Public Charging Networks
Public charging stations make it easy to charge your EV while you’re on the go, whether you’re commuting, shopping, or traveling.
There are many companies that operate networks of public chargers. Payments can usually be made by card at the charger or through an account with the operator. Most networks offer a pay-as-you-go and monthly subscription options. Most networks also offer mobile applications that can help locate stations, manage charging, and manage payment.
Where to Find Public Chargers
- Shopping centers and grocery stores
- Parking garages and lots
- Hotels, restaurants, and workplaces
- Along highways and travel corridors
PlugShare
Use the PlugShare app or website to find EV charging stations near you. See real-time availability, read user reviews, and plan routes with charging stops along the way.
Locate Public Charging Station
Use the U.S. Department of Energy’s Alternative Fueling Station Locator to search for charging stations by location, connector type, or network.
Multi-Unit Dwellings
Installing EV chargers at multi-unit dwellings, such as apartments, condos, and townhouses, can increase property value, attract residents, and support long-term sustainability goals.
Whether you’re a property owner, manager, HOA board member, or resident, the AFDC offers various guides and resources covering everything from charging setup and parking policies to electrical needs and fee structures.