Charging your EV is just as easy as pumping gas. Where, when and for how long depend on what type of charging equipment you use.
Types of Electric Vehicle Chargers
The time to charge an EV depends on multiple different factors. One main factor to consider is how much energy (kWh) is needed, including the total size of the battery and the state of charge (SOC) at the beginning of the charging session. The other major factor to determine charging time is the rate of power output that the EV charging station provides. More details about charging times for each charger type are below. Other factors that impact charging speed include the temperature of the battery, other loads in use while charging such as heating or cooling the cabin, battery deterioration, and the vehicle’s current and voltage limits.
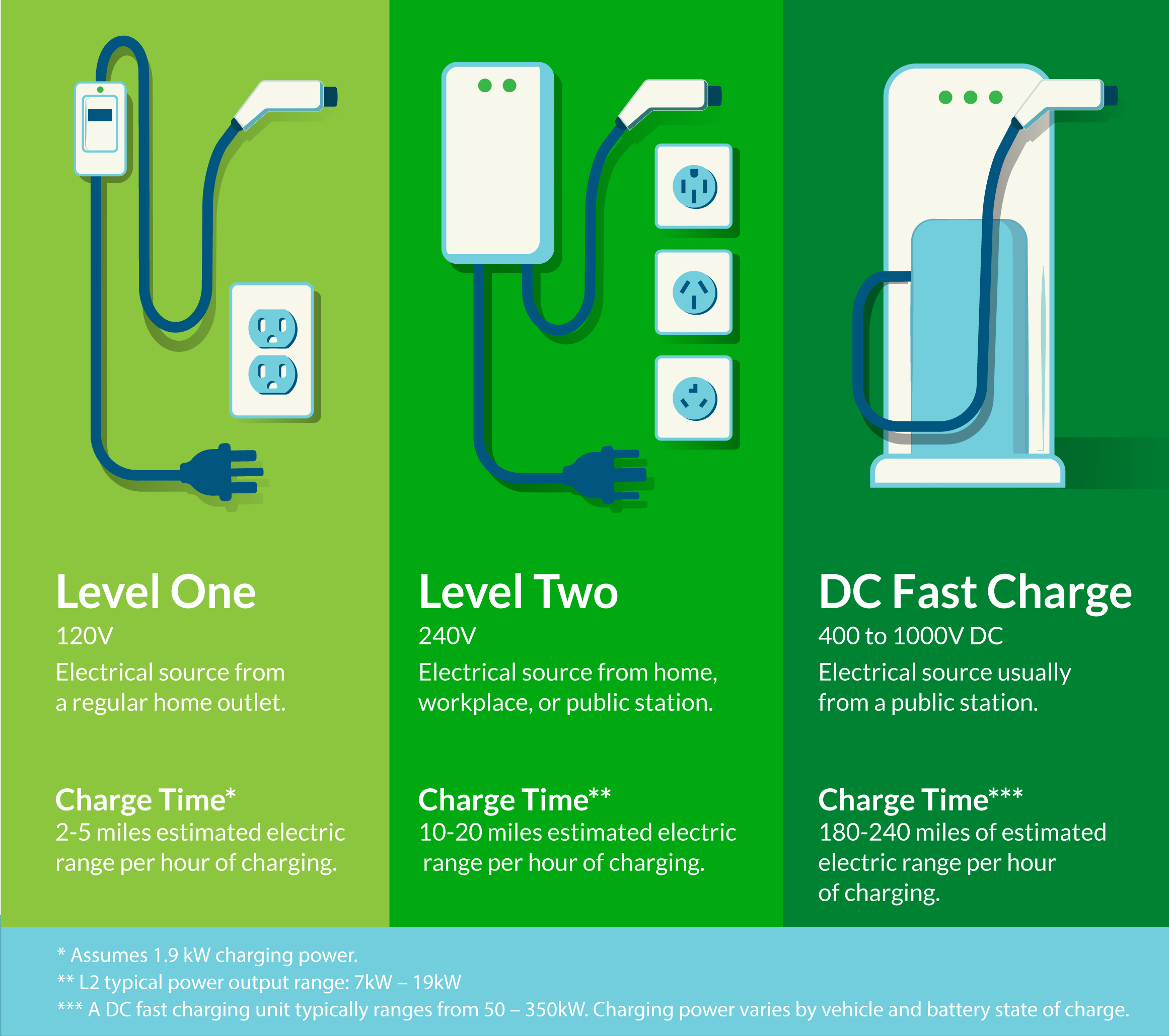
Level 1
chargers use the car’s charge cord to plug into a common 120v outlet, available virtually everywhere. An electric car can maintain more than 40 miles a day if charged overnight at home. Assuming a 60kWh battery, a level 1 charger typically takes 40-50 hours to fully charge. Each hour adds approximately 2-5 miles of driving range.
Level 2
chargers require additional equipment that can be installed by an electrician. In the alternative, they can utilize an existing 240V outlet, just like a clothes dryer. Level 2 charging is also available at public charging stations for a fee based upon kWh used. Assuming a 60kWh battery, a level 2 charger typically takes 4-10 hours to fully charge. Each hour adds approximately 10-20 miles of driving range.
Calculation for EV Charging Time:
To calculate your charging time, divide the amount of charge needed by the power provided by the charger. Use the formula and example below to help estimate your charge time.
Formula:
Charge needed (kWh) / Charger power (kW) = Hours of charging time
Example:
A Tesla Model 3 with an 80 kWh battery size parks at a 7.68kW Level 2 charging station with 20% battery left. They would like to charge their EV to 80%.
Find charge needed:
80% – 20% = 60% needed
80kWh x 0.6 = 48kWh needed
Calculate charging time:
48 (kWh needed) / 7.68 (kW charging speed) = ~6.25 hours of charging time
DC Fast Chargers
are typically available at commercial sites and along highways. Depending on battery size, DC Fast chargers can charge some EVs up to 80% in as few as 20 minutes–1 hour. Each hour adds approximately 180-240 miles of driving range.
- While it is perfectly safe to charge your EV to 100%, the charging will slow down considerably after reaching an 80% SOC. When planning long trips, it often saves time to only charge up to 80% SOC at any given stop.
- Note that each car battery has a maximum power acceptance rate. For example, a car with a maximum of 100 kW would charge at a rate of 100 kW when plugged into a 100 kW fast charger and would still receive a maximum rate of 100 kW even when using a fast charger with a power of 150 kW.